Did you know that the Indian Mutual Fund market can be categorized into various types on the basis of its structure, asset class, investment objectives, speciality, and other such factors? It is important to know the classification of mutual funds as it will help you make wiser decisions in creating a portfolio that meets your financial goals. To help you in your quest, here is a complete guide on the different types of mutual funds.
What is Mutual Fund?
Millions of investors pool their money to form a corpus of the fund. They pool money to achieve the common investment goal. In simple terms, this pooled money is called the mutual fund. The pooled money or the mutual fund is managed by a professional body called the Asset Management Company (AMC).
The investors in a mutual fund are given units to denote their contribution to the pooled funds. Hence, mutual fund investors are called unitholders. The AMC appoints a fund manager to invest and manage the pooled funds.
The fund manager invests the pooled money in various assets as per the defined investment objectives and the returns are distributed to the investors.
The market value of the mutual fund is called Net Asset Value (NAV). The NAV is calculated on a daily basis. NAV is the per-unit market value of the mutual fund.
NAV = [Market value of assets – liabilities & expenses] / Outstanding mutual fund units.
Learn: What is Mutual Fund
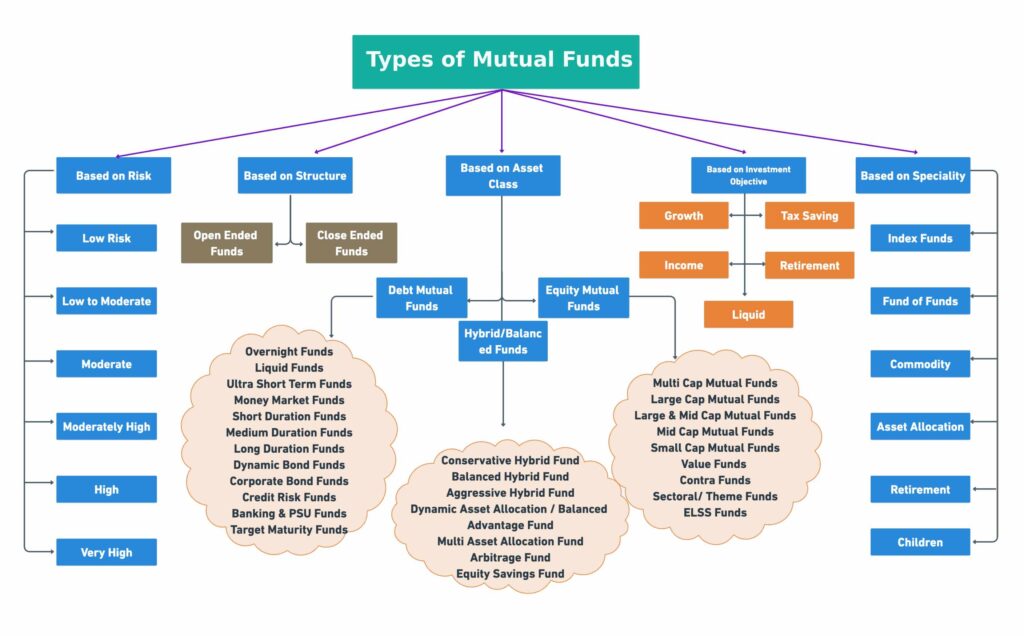
List of Different Types of Mutual Funds Found in India
- Multi Cap Funds
- Large Cap Funds
- Large & Mid Cap Funds
- Mid Cap Funds
- Small Cap Funds
- Value Funds
- Contra Funds
- Sectoral/ Theme Funds
- ELSS Funds
- Overnight Funds
- Liquid Funds
- Ultra Short Term Funds
- Money Market Funds
- Short Duration Term Funds
- Medium Duration Term Funds
- Long Duration Funds
- Dynamic Bond Funds
- Corporate Bond Funds
- Credit Risk Funds
- Banking & PSU Funds
- Money Market Funds
- Hybrid or Balance Advantage Mutual Funds
- Conservative Hybrid Fund
- Balanced Hybrid Fund
- Aggressive Hybrid Fund
- Dynamic Asset Allocation or Balanced Advantage Fund
- Multi Asset Allocation Fund
- Arbitrage Fund
- Equity Savings Fund
- Target Maturity Funds
- Index Mutual Funds
- Fund of Funds
- Commodity Funds
- Asset Allocation Funds
- Retirement Funds
- Children’s Funds
Types of Mutual Fund Based on Structure
The structure of a mutual fund defines the flexibility and ease of sale/purchase of the fund. Based on the structure, the types of mutual funds in India are:
Open-Ended Mutual Funds
Open-Ended Mutual Funds are available for sale or purchase all through the year. The purchase or redemption of these funds is at the prevailing NAVs (Net Asset Values). As a result, investors can continue investing according to their wishes. Further, there is no limit on how much they can invest in open-ended schemes. Open-ended mutual funds are subject to expense ratio due to the fund management charge involved. These funds are highly liquid as the funds do not have any maturity period.
Close-Ended Mutual Funds
In close-ended mutual funds, investors can purchase units only during the initial offer period. Investors can redeem units after the completion of a specified maturity period. Since they lack the liquidity as open-ended mutual funds, close-ended mutual funds trade on the stock exchange to compensate for the same.
One of the most prominent differentiating factors between open-ended and close-ended mutual funds is that the close-ended funds cannot be sold back to the mutual fund house. Rather, they are to be sold on the stock market at the prevailing rates for the share.
Interval Funds
Interval Funds bridge the gap between open-ended and close-ended mutual funds. Much like close-ended mutual funds, they are available as an initial offering and then open for the repurchase of shares by the fund management company at different intervals during the tenure of the fund. Initial unit holders can offload their shares by selling it to the mutual fund house.
Types of Mutual Fund Based on Asset Class
Asset class relates to grouping investments on the basis of common or similar characteristics. They may also be subject to similar laws and regulations. Hence, the classification of Mutual Funds on the basis of its asset class is as follows:
Equity Mutual Funds
- Multi-Cap Fund
Multi-Cap Fund is an open-ended equity scheme that invests in shares of large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap companies. A multi-cap fund allocates a minimum of 65% of the total assets for equity & equity related instruments. Multi-cap funds are the most diversified equity funds. Hence, you have a lower risk as compared to individual large, mid or small-cap focused funds. You get the benefit of stability from large-cap and returns from mid and small-cap stocks. Multi-cap funds are suitable for creating long-term wealth. These are of great value to create a multipurpose corpus. Popular Fund: SBI Focused Equity Fund (G) - Large Cap Fund
Large-cap mutual funds are an open-ended equity scheme with a majority investment in the stocks of large-cap companies. Large-cap mutual funds allocate a minimum of 80% of the pool for investment in equity & equity related instruments of large-cap companies. These mutual funds invest in stable companies with a long track record of robust financial performance with established operations. They can have the lowest volatility among equity mutual funds because large-cap companies’ stock prices fluctuate less and these companies have years of business experience. You have the scope for a steady wealth creation opportunity by investing in large-cap funds. - Large & Mid Cap Fund
Large & mid-cap fund is a mutual fund scheme that brings the benefits of investing in both large-cap and mid-cap companies. Minimum 35% of the total assets of the large and mid-cap fund consists of equity & equity related instruments of large-cap companies. Another 35% of the assets are made up of equity & equity related instruments of mid-cap companies. Large and midcap funds capture the stability offered by the large-cap stocks and the growth opportunities of a mid-cap fund. Popular Fund: SBI Large and Mid Cap Fund (G) - Mid Cap Fund
The mid-cap mutual fund schemes are an open-ended equity mutual fund that predominantly invests in shares of mid-cap companies. Mid-cap mutual funds have a minimum investment of 65% of the total assets in equities & equity related instruments of the mid-cap companies. The mid-cap companies are in a growing phase and have expansion plans. Hence, the mid-cap mutual funds are more aggressive than large-cap mutual funds. The mid-cap mutual funds offer higher returns but also carry a higher amount of risk due to investment in midcap companies. - Small Cap Fund
A small-cap fund is an open-ended equity scheme that invests a major portion in small-cap stocks. The fund invests a minimum of 65% of the total assets of the small-cap mutual fund in equity & equity-related instruments of small-cap companies. Small-cap companies are future companies with very high growth potential. They have the highest risk but also have the potential to generate the highest returns. - Value Fund
Value funds are an open-ended equity scheme that follows a value investment strategy. The portfolio of value funds is constructed on the principles of value investment strategy. The minimum investment in equity & equity-related instruments is 65% of the total assets. You benefit from value funds by the long-term wealth creation opportunities. - Contra Fund
Contra funds are an open-ended equity scheme that follows a contrarian investment strategy. The strategy involves buying and selling in contra (opposite) to the present market sentiments. Contra fund schemes follow a contrarian investment strategy. The fund has a minimum of 65% of total assets invested in equity & equity related instruments. The contra fund helps investors benefit from the contrarian theory by capitalizing on the changing market conditions. - Sectoral/ Thematic Fund
A Sectoral fund is an open-ended equity scheme investing in a particular sector like the pharma, auto or IT sector. Thematic funds are open-ended equity schemes following a particular theme across different sectors. For example export & services fund, business cycle fund, infrastructure fund. Sectoral funds invest a minimum of 80% of total assets in equities & equity-related instruments of a particular sector. A thematic fund invests a minimum of 80% of total assets in equities & equity-related instruments of a particular theme. The sector and thematic funds have high risks of cycles changing or themes dying. Hence, they are high-risk and high return investments. - Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS)
ELSS is an open-ended equity-linked savings scheme with a statutory lock-in of 3 years. These funds invest a minimum of 80% of total assets in equity & equity related instruments in accordance with Equity Linked Saving Scheme, 2005 notified by the Ministry of Finance. ELSS investments allow tax deductions of up to Rs. 1.5 Lakhs under the Income Tax Act, 1961. Compared to other tax saving options ELSS have the lowest lock-in period of three years. ELSS funds have a lock-in period that helps in the reinvestment of returns and ultimately end up generating higher returns. Thus, ELSS serves the dual purpose of tax saving/ planning and generating higher returns from equity investment. Apart from that, you benefit from diversification, professional fund management and low-cost investment through SIP when you invest in an ELSS fund.
Debt Mutual Funds
Debt Mutual Funds park your money in fixed income securities such as treasury bills, bonds, and securities. The debt instruments include Fixed Maturity Plans (FMP), Short Term Plan, Liquid Funds, Monthly Income Plans, Gilt Fund, Long Term Bonds, and more. All the fixed income securities offer a fixed rate of interest and have a maturity date.
These investments are safe as they possess low risk. However, the returns are rarely inflation-beating. Further, in the case of debt funds, TDS (tax deducted at source) is not deducted, so those earning more than Rs. 10,000 on their investment should pay the tax on their own.
Let’s discuss all the different types of funds in detail.
- Overnight Fund
An overnight mutual fund is an open-ended debt scheme that invests in overnight securities. The overnight securities have a residual maturity of a single day. Examples of overnight securities are T-Bills, call money and certificate of deposits having a single day maturity. The overnight fund invests in overnight securities having a maturity of 1 day. They are highly liquid and offer a highly safe investment avenue. Overnight funds help investors park their funds for a few days. They have returns higher than the savings rate offered by many banks. - Liquid Fund
Liquid funds are open-ended debt mutual funds that invest in highly liquid securities. The securities are usually money market instruments like T-Bills, call money, collateral borrowings (CBLO), certificate of deposit (CD’s), and commercial papers (CP’s). A liquid mutual fund invests in debt and money market securities with maturity of up to 91 days only. They are highly liquid and offer a highly safe investment avenue. A liquid mutual fund helps you park excess money for a few weeks up to 3 months. Liquid funds are ideal for creating an emergency fund for various life events like temporary financial crises from job loss and medical emergencies. You can also use liquid funds to manage your monthly expenses and for making provisions. The best part is that your money is accessible in a day or two of the redemption requests. Thus, the liquid fund helps you earn a higher return than the savings account rate. - Ultra Short Duration Fund
Ultra short duration funds are an open-ended scheme that invests in debt instruments with Macaulay duration lying between 3 months and 6 months. In layman terms, Macaulay’s duration is the time an investor would take to get back all his invested money in the bond by way of periodic interest as well as principal repayments. The Macaulay duration for a portfolio is calculated as the weighted average time period over which the cash flows on its bond holdings are received. Ultra-short duration funds too are highly liquid and offer a relatively stable investment avenue. Investors benefit from a longer duration fund that generates a slightly higher income and reinvestment opportunity. Using ultra-short duration mutual fund you can create a corpus for purchasing a dream bike or retire an existing short-term loan. - Money Market Fund
Money Market Fund is an open mutual fund scheme that invests majorly into money market instruments like T-bills, CPs, and CDs. These funds invest in money market instruments having maturity up to 1 year. They are highly liquid and offer a highly safe investment avenue. Money market funds are best for a risk-averse investor that combines a better yield and safe investments. - Short Duration Fund
Short duration fund is an open-ended short term debt scheme investing in instruments with Macaulay duration between 1 year and 3 years. They offer a stable investment avenue with good returns. Short duration funds are best in a rising interest rate scenarios. You benefit from additional interest income and a reinvestment opportunity. The low duration fund is best for conservative investors who want to grow their money without fluctuations. The short duration fund is suitbale for life goals of expensive foreign vacations and meeting wedding expenses. - Medium Duration Fund
Medium duration fund is an open-ended scheme that invests in debt securities that have a Macaulay duration between 3 years and 4 years. These funds offer a relatively stable investment avenue with good returns. The fund provides capital protection and higher yields. The fund consists of debt & money market instruments like Government securities, T-bills, CDs and CPs. Medium duration funds are helpful in creating a corpus of funds for conservative investors who want to build capital without taking a risk like aggressive equity investors - Long Duration Fund
Long duration mutual fund is an open-ended scheme that invests primarily in debt instruments with Macaulay duration greater than 7 years. These long duration funds are best in a falling interest rate scenarios. Because the interest rate is inversely proportional to bond prices. Generally, the long duration funds have the highest yield among all the duration funds. They also carry the highest interest rate risk among the duration funds. The fund invests in corporate bonds, Govt. securities, T-bills, CDs and CPs such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is greater than 7 years - Dynamic Bond Fund
A dynamic bond fund is an open-ended dynamic debt scheme that invests in debt instruments across the duration. The fund offers flexibility to manage duration in different market scenarios. In a sense, they increase maturity in falling interest rate scenarios so that you can enjoy higher interest income. Likewise, they decrease the maturity in a rising interest rate scenario. Hence, you do not need to manage the fund actively. - Corporate Bond Fund
Corporate bond funds are an open-ended scheme that invests predominantly in the highest-rated corporate bonds. The fund investments are in AAA-rated bonds from established large companies. The fund invests a minimum 80% of the total assets in the highest-rated (AAA) corporate bonds. The instruments include bonds, debentures, commercial papers, and structured obligations. - Credit Risk Fund
Credit risk fund is an open-ended debt scheme that invests in below highest-rated corporate bonds, i.e in AA or A-rated debt papers of companies. The fund invests a minimum of 65% of the total assets in debentures, commercial papers, and bonds of companies having below the highest-rated instruments. - Banking and PSU Fund
Banking and PSU fund is an open-ended mutual fund scheme predominantly investing in the debt instruments of banks, Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), and Public Financial Institutions. The fund invests a minimum of 80% of the total assets of the fund in debt instruments like Tier I and Tier II bonds of banks and PSUs. - Money Market Mutual Funds
The money market mutual funds invest in liquid assets. Owing to a high degree of liquidity, they are also known as the cash market or capital market. Government or financial institutions such as banks or corporations form the backbone of money market mutual funds through securities such as bonds, dated securities, and certificates of deposits, T-bills, etc. Normally, it is ideal for those who wish to park their excess money for the short term.
Balanced Advantages / Hybrid Funds
Also known as hybrid funds, balanced mutual funds in India are a mix of assets, such as bonds and stocks. The ratio of fixed income to equity could be fixed or variable. Normally, these funds invest in equities and debt in the 40:60 proportion, with either of the two outweighing the other. Accordingly, the risk and returns associated with this mutual fund balance each other out. Due to their characteristics, balanced mutual funds can be thought of as an intermediary of debt and equity funds.
- Conservative Hybrid Fund
Conservative Hyrbid funds must invest at least 10% to 25% in equity & equity-related instruments and 75% to 90% in Debt instruments. - Balanced Hybrid Fund
Balanced Hybrid Funds must invest at least 40% to 60% in equity & equity-related instruments and 40% to 60% in Debt instruments. - Aggressive Hybrid Fund
Aggressive hybrid funds must invest 65% to 80% in equity & equity related instruments, and 20% to 35% in Debt instruments - Dynamic Asset Allocation or Balanced Advantage Fund
Balanced Advantage funds must invest in equity/ debt that is managed dynamically (0% to 100% in equity & equity-related instruments; and 0% to 100% in Debt instruments). - Multi-Asset Allocation Fund
Multi-asset funds must invest in at least 3 asset classes with a minimum allocation of at least 10% in each asset class. - Arbitrage Fund
Arbitrage funds are funds that follow the arbitrage strategy and invest a minimum of 65% in equity & equity-related instruments. - Equity Savings
Equity savings funds invest a minimum of 65% in equity and equity-related instruments and a minimum of 10% in debt instruments and in derivatives.
Types of Mutual Fund Schemes Based on Investment Objectives
What is the end-goal of your investment? Is it to increase wealth? Or Is it to save taxes? Or Is it to make short-term gains? Depending on the ultimate investment objective, the mutual funds can be classified as:
- Growth Mutual Funds
Growth mutual funds invest the money primarily in growth-sector equity stocks. As their name suggests, the main objective of Growth Mutual funds is capital appreciation. They are not suitable for long-term investments and also occupy a high-risk grade. - Income Mutual Funds
Fixed-income mutual funds are a sub-class of debt mutual funds. These funds distribute the money in a mix of income assets such as debentures, bonds, securities, and certificates of deposits. Skilled fund managers manage Income mutual funds and are responsible for maintaining capital protection while also offering regular income to the investors. Such an investment is ideal for risk-averse investors who wish to park their money for at least 2 to 3 years. - Liquid Mutual Funds
Liquid mutual funds are also a sub-class of debt mutual funds. The fund invests the money in short-term and ultra-short-term instruments like commercial papers, bank certificate of deposits, treasury bills, and more. The main purpose of liquid mutual funds is to provide liquidity. These investments are low on risk and offer moderate returns. Investors looking for short-term investment opportunities should park their money in best liquid mutual funds. - Tax Saving Mutual Funds
Tax Saving Mutual Funds, or Equity-Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS), are funds that invest the money in equity. The money invested in these schemes is eligible for deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. While they are high on risk, they can offer a handsome return if the fund performs well. - Pension Funds
Pension mutual funds are really long-term investments that offers regular returns after the investor retires. These funds split the investment between equity and debt instruments so that the equity component offers higher returns while the debt component balances the risk while providing low but steady returns. Investors can draw their returns as a lump sum amount or as a fixed pension, or in a combination of the two.
Types of Mutual Funds Based on Specialty
SEBI has also categorized certain funds as speciality funds, these are:
- Index Mutual Funds
Index Mutual Funds, also known as Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), is a class of mutual fund schemes that not only track but also replicate the asset allocation of a certain index. Normally, index mutual funds must have an investment portfolio that is at least 95% similar to the index that it is tracking. Since these funds are passively managed, the expense ratio is low.
The key difference between ETFs and Index Funds is that ETFs trade on the stock market, while Index Funds do not. Index funds are an open-ended scheme replicating/ tracking a particular stock index. For example, the Nifty Index Fund will have a composition similar to the Nifty 50 stock index. The fund invests a minimum of 95% of total assets in securities of a particular index which it replicates/ tracks. The index funds follow a passive investment style. Index funds investors benefit from diversification, passive fund management, and lower costs. - Fund of Funds
As the name indicates, Fund of Funds (FoF) invests in other mutual funds (which could be Domestic or International) and the resultant returns on the investment vary on the basis of the performance of the target fund. Such investments are considered to be safer as the Fund of Funds holds a diversity of funds, which adjusts the portfolio and balances the risk. These funds are also known as Multi-Manager Funds. Fund of funds is an open-ended mutual fund scheme that invests in other mutual fund schemes.
A minimum of 95% of the total assets of the Fund of Funds is invested in the underlying mutual fund scheme. Like, a FoF scheme investing (95% of the corpus) in global funds. Depending on the scheme objective the Fund of funds can invest in domestic or overseas (global) mutual fund schemes. The pooled money is used in investing in other mutual fund schemes rather than in assets like equity or bonds. The FoF offers investors a large diversified portfolio, which reduces risk and provides an opportunity to invest, sometimes globally, with a small amount of capital. Quantum Equity FoF Fund (G) and Franklin India Life Stage FoFs-20 (G). - Commodity Mutual Funds
Much like sector mutual funds, commodity mutual funds invest in companies that are functioning in the commodity market. The returns of these funds depend on the performance of the commodity or the stock of the company that produces the commodity. Further, the returns are not periodic in nature. Such investments can be high-risk and for those wishing to diversify their portfolio. Examples- Investors in India can directly invest in Gold, which is a commodity, or put their money in Gold Funds (commodity-linked mutual funds such as Kotak Gold Fund. Other commodities include Oil, Silver, etc. - Asset Allocation Funds
Asset Allocation Mutual Funds combine debt, equity, and sometimes even gold, in an optimum ratio. Due to the diversity in the asset portfolio, these funds are highly flexible. The ratio of investment could depend on the prevailing market trends, preset formula, or based on a fund manager’s skill or experience. While they sound like Hybrid Funds, Asset Allocation Funds require greater expertise of the fund manager in choosing and allocating the bonds and stocks. - Retirement Fund
The funds are hybrid in nature that invests a major portion of the corpus in equity for the long-term. The retirement fund’s objective is to build wealth for retirement by providing long-term capital appreciation and income. The funds provide steady income post-retirement using convenient withdrawal options. They are also known as pension funds. A retirement fund is an open-ended retirement solution-oriented scheme that has a lock-in period of 5 years or till the retirement age (whichever is earlier). The investors have a dedicated mutual fund for building a corpus of the fund to cover the lifestyle expenses after retirement. - Children’s Fund
Children’s fund is an open-ended fund for investment for children having a lock-in for at least 5 years or till the child attains the age of majority (whichever is earlier). These funds are hybrid funds having exposure to both equity and debt instruments. The fund discourages withdrawal by having a lock-in period so that you do not utilize the funds for other purposes. The mutual fund focuses on creating wealth for children that can have various purposes like higher education and marriage expenses.
Types of Mutual Funds Based on Risk
Following are the types of mutual funds based on risk:
- Low Risk
Low-risk mutual funds give returns that are relatively stable. This does not, however, imply that the schemes are risk-free. Low-risk funds give higher returns and are tax-efficient compared to conventional assets such as fixed deposits. Therefore, the funds are suited for investors who are risk-averse.
Debt mutual funds invest in low-risk money market products, government bonds, etc. Consequently, the associated risk with these instruments is reduced. There are numerous schemes within the area of debt funds. These include liquid, dynamic bonds, gilt, and ultra-short-term funds, among others. Typically, debt funds are subject to interest rate risk and credit risk. However, investing in bonds with higher ratings will assist mitigate the risk. Since these funds entail minimal risk and seek optimal returns, they are an excellent choice for short-term investments.
Furthermore, they are ideal for generating regular income. Also, you can liquidate the investments at any time. Low-risk funds do not have any lock-in period. Thus, access to funds is never an issue with low-risk funds. - Medium Risk
Mutual funds with moderate risk invest in both equities and debt securities. The hybrid portfolio enables the funds to deliver returns that exceed inflation over the medium term. These funds are less hazardous than pure equity mutual funds but slightly riskier than pure debt funds (low-risk funds). The ideal investment tenure is three to five years for moderate-risk mutual funds.
Different types of mutual funds with moderate risk have distinct investment objectives. For example, debt hybrid funds include dynamic bond funds. The objective of these funds is to create returns by switching between short-term and long-term bonds in response to changes in interest rates.
On the other hand, dynamic asset allocation funds tactically shuffle between equity and debt schemes. In reaction to market fluctuations, the fund’s asset allocation is modified to give the highest return with the lowest risk. On the other hand, short-term funds offer returns that are more or less stable with moderate levels of risk.
Therefore, moderate risk funds are appropriate for investors who do not have a high-risk tolerance but are ready to accept a certain degree of risk. Moreover, several of these funds offer more or less stable returns over the medium term, making them an excellent alternative for investors seeking inflation-matching returns or, in the case of equity funds, returns that exceed inflation. - High Risk
High-risk mutual funds have a greater chance of generating high returns compared to other funds. In addition, these funds are extremely volatile, and there is no guarantee of return. High-risk funds invest in volatile securities, and as a result, their returns are unpredictable.
Since the funds invest in high-risk securities, it is prudent to monitor your investments constantly. Periodically monitoring the funds will assist you in limiting any potential downside risk. In addition, you can assess the fund’s performance in light of the fluctuating market dynamics.
Not all high-risk funds are equity-based mutual funds. Debt schemes that invest in securities with low ratings are also highly risky. Moreover, having a long-term investment horizon is almost a must for investing in high-risk mutual funds. With a long-term investing horizon, it is possible to average out the fund’s volatility. Consequently, the possibility for greater returns increases.
As the phrase goes, the greater the risk, the greater the returns – high-risk mutual funds are more likely to provide substantial returns than low- or moderate-risk schemes. However, it is essential to remember that risk is a relative metric, and caution should be exercised while selecting funds.
Conclusion
Mutual fund investment has a lot of benefits in terms of diversification, professional management, low cost, and a dedicated fund manager. But you need to know your investment goals before you make a mutual fund investment.
An equity fund is best for investors having a long-term investment horizon. Debt mutual funds are helpful for investors looking for low volatility short-term investment options.
Now that you have gained some understanding of the various types of mutual funds, you will be in a better position to compartmentalise your investments. Once you have an understanding of what you expect out of your investments, you will be in a better position to pick the funds that suit your requirements and your goal. Do remember to factor in the risk involved against all the different types of mutual funds.
Normally, all types of mutual fund schemes carry some amount of risk, no matter how small. Thus, it is important that as an investor, you should go through their policy documents before investing. This one small act can grant you knowledge about the various facilities offered by the fund house and where your money gets invested.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are multiple types of mutual funds, and the best depends on the investor’s investment objective. For example, mutual funds can be categorised based on their structure (open-ended or close-ended or interval funds). They can also be classified based on the asset class, such as Equity, Debt and Hybrid Funds. Furthermore, under each category, there are different types of mutual funds.
Each category of the fund has a different investment objective and different levels of risk associated with them. An equity fund is best for investors having a long-term investment horizon. While debt mutual funds are helpful for investors looking for low volatility short-term investment options. Similarly, hybrid funds are suitable for investors looking for moderate to low volatility medium-term investment options.
Therefore, a mutual fund that is best for an individual doesn’t necessarily have to be the best for the other individual. A best mutual funds is one whose fund objective perfectly aligns with the investor’s profile and investment objective. Hence, on the basis of the investment horizon, objective and risk understanding, one can shortlist mutual funds that best suit their purpose.
Mutual funds are market-linked instruments and hence are subject to market volatility. Therefore, no mutual fund is 100% safe. However, mutual funds have different levels of volatility. In other words, equity mutual funds purely invest in equities and are highly volatile to the changing market dynamics. On the other hand, debt mutual funds invest across different debt instruments issued by the government and corporates, and hence are slightly less volatile in comparison to equity mutual funds.
Unlike bank deposits or government bonds, mutual funds do not guarantee returns.
The three main groups of mutual funds are equity, debt and hybrid mutual funds. Equity funds invest in stocks of companies and thus are high-risk investments. In contrast, debt mutual funds invest in debt securities like bonds, government securities, etc. Thus, these are low-risk schemes. On the other hand, hybrid funds invest across both equity and debt schemes and thus are moderate-risk funds.
Based on Structure: Open-Ended, Close-Ended, and Interval Funds
On the Basis of Asset Class: Equity, Debt, and Hybrid/ Balanced Funds
Based on Investment Objectives: Growth, Income, Liquid, Tax Saving, and Pension Funds
Based on Specialty: Index, Fund of Funds, Commodity, Asset Allocation, Retirement, and Children’s Funds.
For beginners who are looking to invest in mutual funds can start their journey by investing in large-cap funds. Large-cap mutual funds invest in large-cap stocks. These stocks belong to companies that are market leaders in their sectors. Thus, the funds are not extremely volatile like the mid-cap or small-cap funds.
Popular Equity Mutual Funds:
Canara Robeco Bluechip Equity Fund
Popular ELSS Mutual Funds:
Mirae Asset Tax Saver Fund
Popular Liquid Funds:
ICICI Prudential Liquid Fund
Equity investments can be grouped by the size of company (large, mid, small); or market (Indian, US) etc. These are called sub-asset classes and help portfolio managers target their investments better.























Show comments