Investing is the act of putting your money to work over a period of time with the goal of generating positive returns—profits that exceed your initial amount. In essence, it involves directing resources, typically capital, into ventures or assets poised to produce future income, profit, or gains, thereby allowing your wealth to grow beyond its original value.
What are the Types of Investment?
Understanding the different types of investments and their characteristics can help you grow wealth and achieve your financial goals.The type of returns you get depends on the investment you choose. Real estate can provide both rent and capital gains, while stocks might offer dividends and the potential for price appreciation.
Definition of Investment
Investment refers to the act of allocating resources, typically money, into a venture or asset with the expectation of generating income, profit, and gains while also maintaining or increasing the purchasing power of one’s capital in the face of inflation. It involves putting your money to work for a period of time in a project or undertaking to generate positive returns. Investing can be done directly or indirectly and can involve a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or even gold. By investing, you aim to grow your wealth and achieve your financial goals over time.
Importance of Investment
Investing is essential for individuals, businesses, and governments to achieve their financial goals and objectives. For individuals, investing allows you to grow your wealth, achieve financial independence, and secure your future. By investing in different types of assets, you can build a diversified portfolio that helps you manage risk and maximize returns. For businesses, investing in new projects, technologies, and markets can drive growth, increase competitiveness, and improve profitability. Governments invest in infrastructure, education, and healthcare to promote economic development and improve the quality of life for their citizens. Understanding the importance of investing in various sectors can help you make informed decisions and achieve long-term financial success.
Objectives of Investment
The main objectives of investment are to grow your capital, generate income, and secure your financial future. By investing wisely, you aim to earn returns that outpace inflation, helping your money grow in real terms.
How does the investment work?
Investing is a way to make your money work for you. But what is investment exactly? It’s when you spend money today on something that can grow and bring you more money in the future. You can invest in various options such as mutual funds, PPF, stocks, bonds, and real estate. For example, when you buy stocks, bonds, or land, you hope to earn money through dividends, interest, or the value going up. This is one of the key types of investment people use to build wealth.
Investing vs. Saving
Investing is different from saving. Saving means saving money for future use, like in a savings account. It keeps your money safe but doesn’t grow much. On the other hand, investing involves buying assets to increase their value over time. While saving typically suits immediate or short-term goals due to its low risk and high liquidity, investing can be tailored for both short- and long-term objectives—like a child’s education, marriage, or retirement planning—depending on the strategy used. Understanding the value of investing helps you prepare for future financial needs.
The Risks and Rewards of Investing
All investment types come with some risk. Stock prices can be volatile, sometimes rising or falling sharply. Poor company performance may reduce your investment’s value, and economic factors like interest rates and inflation can affect overall returns. A lack of diversification—focusing too much on a single company, industry, or asset class—can increase your exposure to these risks. Still, with careful planning and a long-term view, investing can help you achieve your financial goals.
Investing isn’t just about money. It can also mean taking actions that help you earn more in the future. For example, learning new skills or getting more education can lead to better job opportunities and higher income. This is another way to understand investment and how it can benefit you.
Finding the Best Investment Options
With so many choices, deciding where to invest money in India can be tough. Understanding the types of investments in India is crucial to align your choices with your financial goals. If you’re looking for the best investment options in India or wondering which is the best investment plan in India for the middle class, a financial advisor can help. They can guide you through different investment types and create a plan that fits your goals. While they charge a fee, their expertise can help you reach your financial objectives more effectively.
Looking for investment? Check out best investment option in India
Investment Benefits
Investing offers numerous benefits, including:
Power of Compounding
The power of compounding refers to the ability of an investment to generate returns on its returns, resulting in exponential growth over time. This means that even small, consistent investments can add up to significant wealth over the long term. For example, if you invest in a mutual fund that earns a 10% annual return, the returns you earn each year will also start earning returns. Over time, this compounding effect can lead to substantial growth in your investment portfolio.
Beating Inflation
Investing can help individuals beat inflation by generating returns that exceed the rate of inflation. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your money over time, meaning that the same amount of money will buy fewer goods and services in the future. By investing in assets that offer higher returns, such as stocks or real estate, you can preserve and even increase your purchasing power. This ensures that you can maintain your standard of living and achieve your financial goals, even in times of rising prices.
How to Invest?
For those wondering where to invest money in India or searching for the best investment options in India, it’s important to understand your goals and the way you are going to invest. Would you like to manage your investments yourself, or would you prefer professional assistance?
Do-It-Yourself (DIY) Investing
DIY investing means you make all your own decisions about your money and have full control over where you invest. This is good for people who have the time, knowledge, and confidence to handle their investments independently. Many DIY investors use online brokerages because they have low fees and are easy to use.
However, successful DIY investing requires a solid understanding of market trends and the ability to manage one’s emotions during market fluctuations. If you’re a middle-class individual in India asking which is the best investment plan for the middle class, DIY investing could be a viable option if you’re willing to put in the effort to educate yourself.
Robo-Advisor Investing
If you prefer a simpler way, robo-advisors can help. They are computer programs that manage your investments automatically. They look at how much risk you’re comfortable with and your financial goals and then suggest investments for you. This option doesn’t cost much and is great for people in India looking for the best investment options without knowing much about the market.
Robo-advisors can help you plan for retirement, manage trusts, and handle other accounts. Thanks to today’s technology, they can do many things that human advisors do, but with less human involvement.
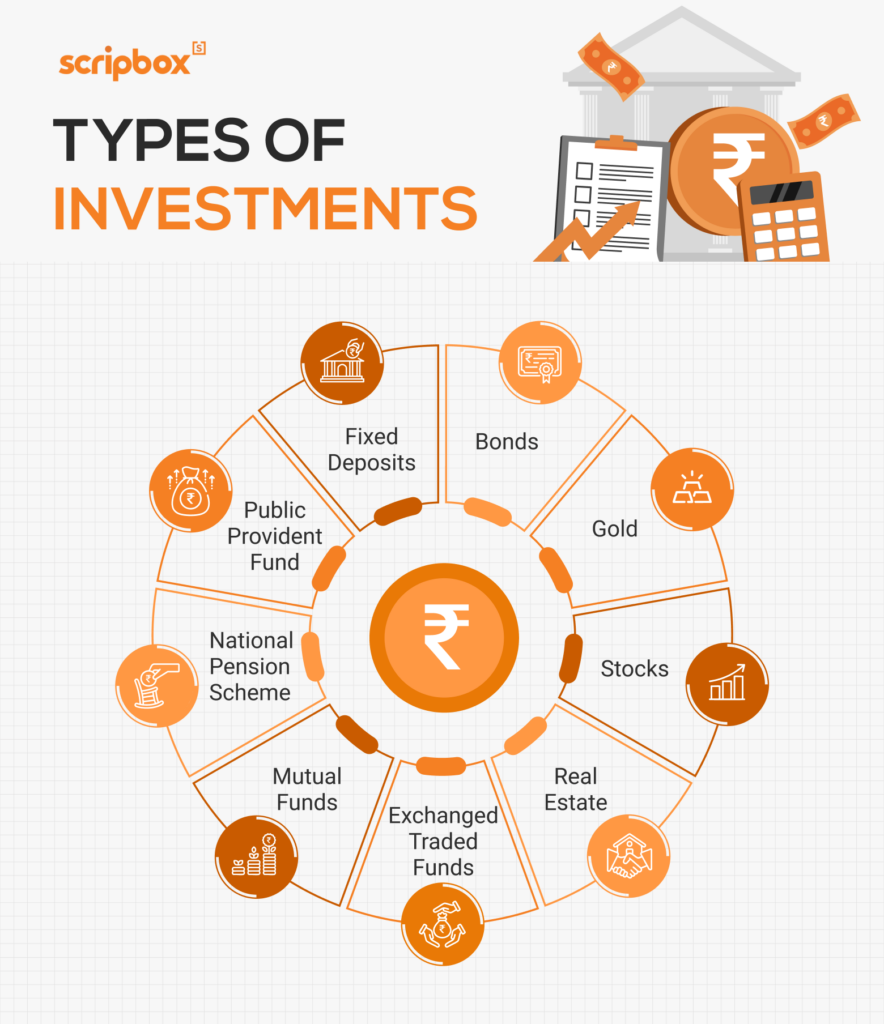
Types of investments
There are many types of investment available in the market, and we can divide them into three main categories:
1. Fixed-Income Investments
These investments offer guaranteed returns in the form of interest, making them low-risk options. Examples include:
- Fixed Deposits (FDs)
- Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- Government Bonds
2. Market-Linked Investments
Market-linked investments don’t guarantee returns because they depend on market movements. They are considered high-risk but can provide higher returns when the market does well. Examples are:
- Stocks
- Mutual Funds
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
3. Alternative Investments
Investments that don’t fit into fixed-income or market-linked categories are called alternative investments. These include:
- Real Estate
- Gold and Precious Metals
- Commodities
1. Fixed deposits
Banks and financial institutions usually offer fixed deposits, popularly known as FDs. FDs provide guaranteed returns and are the most popular investment type in India. They have a tenure ranging between 7 days and ten years. Fixed deposit interest rates vary between 3%-7%. Moreover, senior citizens are offered additional interest in their FD investments. The FD interest rates are higher than the savings account interest rate. The interest payments are made monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, annually, or at the time of maturity as per the investor’s choice.
Investment in tax-saving FDs qualifies for tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act 1961. Moreover, the interest income is taxable per the individual investor’s income tax slab rates. If the interest income exceeds INR 40,000 per annum (INR 50,000 for senior citizens), the bank levies a TDS of 10% (20% if PAN cards are not disclosed).
2. Bonds
Bonds are fixed-income instruments offering investors a fixed interest rate against invested money. The investors lend money to the Government and corporations and get regular income through interest. Bond issuers are the borrowers who raise money publicly or privately to fund various projects. A bond is an instrument that includes information on the interest, due date, maturity date, and bond terms. Investors of bonds are paid the entire amount after the bond expires (upon maturity). Investors can also sell the bond at higher prices before maturity in the secondary market and get profits.
Bonds are considered low-risk investments. However, there are certain risks attached to them. The most common risk is the default risk. Bond issuers can default on interest and principal repayment. However, investors can assess the risk in the bond before investing. They can do so by checking the credit rating of the bond. Bonds with higher credit ratings are less likely to default on the payments than bonds with low credit ratings. Bonds with an AAA rating are considered the safest. Having bonds in one’s portfolio helps investors diversify their investment risk.
3. Public Provident Fund (PPF)
The Public Provident Fund is one of the post office savings schemes launched by the National Savings Institute. However, some private and nationalized banks are authorized to accept PPF investments. Returns from the scheme are guaranteed as the Government of India backs it. Hence, they are considered low-risk investments. Furthermore, the PPF investments come with a 15-year lock-in period. Also, if the investor wishes to extend the scheme, they can do so within 5 years. Furthermore, for tax savings, one can invest in PPF.
The PPF interest rates are announced every quarter. The current rate is 7.10% for (Jul – Sep 2024). Also, the interest payments are made every year on the 31st of March. However, the interest is calculated monthly on the minimum PPF balance between the 5th and 30th of each month.
Investments up to INR 1,50,000 per annum qualify for tax exemption under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act 1961.
4. Stocks
Stock investment is known as equity investment. Buying stocks or shares gives investors a part of the ownership of that company. Investors invest in stocks to earn regular income in the form of dividends and gain from capital appreciation. When stock prices rise, investors can benefit from selling the shares.
Stock returns are market-linked, so they are considered the riskiest investment type. Share prices fluctuate based on market demand and supply and market sentiments. A bullish sentiment will lead to an unexpected rally in the market, while a bearish sentiment will lead to a drop in share prices.
Investing in the share market should be done with a long-term investment horizon. In the short term, the market will fluctuate, which might lead to unexpected losses. Investors need to be patient while investing in inequities.
Investors need a demat and trading account to invest in shares. A demat account holds the shares, while a trading account facilitates the purchase and sale of shares. Short-term capital gains from stock investing (below one year) are taxable at 20%. At the same time, long-term capital gains are taxable at 12.5% if the gains are above INR 1,25,000 per annum.
5. Mutual funds
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from investors to invest in assets like equity and debt. A mutual fund strategically invests in shares, government bonds, corporate bonds, Real Estate and other assets. The fund house appoints a portfolio manager or fund manager to manage the mutual fund.
Every mutual fund has an investment objective, and the fund’s investments revolve around this. Mutual funds can be of several types based on the assets. For example, equity, debt, and hybrid funds are three types of mutual funds based on the asset class. Similarly, funds can be categorized based on their strategy, structure, and investment options. There are also mutual funds that offer tax benefits. These are called Equity Linked Savings Scheme. or ELSS funds. Investment in these funds qualifies for tax deduction under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961.Returns from mutual funds are taxable according to the investment holding period. Short-term capital gains are subject to short-term capital gains tax (STCG tax), and long-term capital gains are subject to long-term capital gains tax (LTCG tax). Furthermore, tax rates vary for equity and debt mutual funds.
6. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF)
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a passive investment option that usually replicates the underlying index. In other words, an ETF portfolio matches the composition of an Index in the same proportion. An ETF mimics and tracks the performance of the index. Hence, ETFs are not actively managed by a portfolio manager. Furthermore, exchange-traded funds do not attempt to outperform their respective index.
There are different types of ETFs, such as equity, bond, currency, and commodity ETFs. One can easily buy or sell them on the stock market.
7. Gold Investments in India
Gold is not just an investment option but also holds a deep sentimental value. Today, investing in gold has become easier with options like gold bonds and gold ETFs, which are gaining popularity.
While gold doesn’t provide dividends, unlike some other investment options, it is considered one of the safest forms of investment. It’s a liquid asset that can offer returns beating inflation, making it one of the best investment options in India for protecting wealth.
8. Real Estate
Real estate is another key investment type in India. It involves buying and managing properties like land and buildings. Investors aim to sell these assets at higher prices later or earn regular income through rent. Real estate offers long-term growth for those wondering where to invest money in India.
Investing in real estate has become more accessible with Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). REITs let you own a part of a property with a smaller investment. You can earn a steady income from dividends, which come from the rental income of the properties. This makes real estate a good option for medium—to long-term financial goals, especially for the middle class seeking the best investment plans in India.
9. National Pension Scheme (NPS)
The National Pension Scheme (NPS) is a suitable retirement scheme. Investors who wish to receive regular income after retirement and save tax can invest in NPS. The Central Government backs it; hence, it is considered a low-risk investment.
Investors can invest at regular intervals during their employment. The scheme allows the investor to withdraw a percentage of the accumulated amount post-retirement. The investor also receives the remaining amount monthly as a pension post-retirement.
NPS has two types of accounts: NPS Tier I Account and NPS Tier II Account. The Tier I account is a default account, while the Tier II account is a voluntary account.
NPS investments up to INR 1,50,000 qualify for tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961. Furthermore, an additional INR 50,000 is eligible for tax deduction under Section 80CCD of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Things to keep in mind while investing
Before you decide where to invest money in India, keep these points in mind.:
1. Investment Objective
Think about what investment means to you and what you want to achieve. Your objectives might be saving for education, buying a house, or planning for retirement. Not all investment types suit everyone. What might be the best investment plan in India for the middle class for one person might not be the same for another. Make sure your investment choices match your personal goals.
2. Investment Horizon
This is how long you plan to keep your money invested. Different investments work better for different time frames. Option options like fixed deposits (FDs) or money market instruments might be good for short-term goals. For long-term goals like retirement, you might consider stocks or mutual funds. Knowing your time frame helps you pick the best investment options in India for your needs.
3. Risk
All investments involve some risk. Investment options like stocks can be classified as high-risk options as their prices change daily, whereas fixed deposits are usually safer as they offer guaranteed returns.
It’s important to look at how an investment has performed in the past, but remember that past performance doesn’t guarantee future results.
4. Costs and Expenses
Investing isn’t free. There might be fees for buying or selling investments. Mutual funds charge management fees, and some investments charge penalties if you take your money out early. Look for low-end investments so you can keep more of your returns.
5. Liquidity
Liquidity means how easy it is to turn your investment into cash. Some investments, like stocks or mutual funds, are easy to sell quickly. Others, like real estate, can take a long time to sell.
6. Lock-In Period
Some investments require you to keep your money invested for a certain time. For example, a Public Provident Fund (PPF) has a lock-in period of 15 years. Fixed deposits might lock your money for 5 years. Knowing the lock-in periods helps you plan, so you’re not surprised if you need the money sooner.
Check out Scripbox Recommended Liquid Funds
7. Taxation
Returns from investments may be taxed. For example, gains from mutual funds can be taxed depending on how long you hold them. Some investments, like PPF, offer tax benefits, and the returns are tax-free. Understanding the tax rules can help you get the most out of your investments. You can use an income tax calculator to calculate your tax liability.
Check Out Momentum Indicators
READ MORE
- Best Investment Plan to Invest in India
- Best Performing Mutual Funds in India
- Best Tax Savings Investment Plans
- Latest Nav for all Mutual funds
- How to Calculate Yield to Maturity
- Fixed Income Instruments
- Best Investment Options for Women
- Best Investment Plan for Middle Class
- Best Short Term Investment Plans
Related Articles
- What are the Types of Investment?
- Investment Benefits
- How to Invest?
- Types of investments
- 1. Fixed deposits
- 2. Bonds
- 3. Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- 4. Stocks
- 5. Mutual funds
- 6. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF)
- 7. Gold Investments in India
- 8. Real Estate
- 9. National Pension Scheme (NPS)
- Things to keep in mind while investing
























Show comments