The money market is referred to as dealing in debt instruments with less than a year to maturity bearing fixed income. In this article, we will cover the meaning of money market instruments along with its types and objectives.
What are Money Market Instruments?
Money Market instruments, such as Treasury Bills, Certificates of Deposit, Commercial Paper, and Call Money Market instruments, are short-term financial tools that play a vital role in the Money Market. They are backed by trusted entities like the government and large corporations and can easily be converted to cash when needed.
Common examples include:
- Treasury Bills: Government-issued securities that mature in a short time.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Savings certificates with a fixed interest rate and maturity date.
- Commercial Paper: Unsecured loans issued by companies to meet short-term financial needs.
- Call Money Market: Very short-term loans, often overnight, between financial institutions.
A money market fund is another important component, offering a safe and liquid investment option by investing in short-term, low-risk debt instruments.
By using Money Market instruments, investors can earn a small return on their surplus funds while borrowers can meet their short-term funding requirements.
What is the Money Market?
Definition and Functions of the Money Market
The money market is a financial market where short-term debt securities with one year or less maturities are traded. It provides a platform for borrowers and lenders to interact and facilitate short-term borrowing and lending. The primary function of the money market is to enable governments, banks, and other large institutions to sell short-term securities to fund their short-term cash flow needs. This market is essential for maintaining liquidity in the financial system, allowing entities to efficiently manage their immediate financial obligations.
Importance of the Money Market in the Economy
The money market plays a crucial role in the economy by providing liquidity and facilitating the smooth functioning of the financial system. It enables governments and corporations to raise short-term funds to meet their immediate cash needs, ensuring they can continue their operations without interruption. For individual investors, the money market offers a low-risk investment option where they can park their excess funds and earn a modest return. The money market helps maintain economic stability and growth by supporting these various needs.
Objectives of the Money Market Instruments
The Money Market plays an important role in controlling our country’s market, and this is why it’s important to us.
Money market funds are essential for providing liquidity and safety to investors, ensuring that their short-term financial needs are met efficiently.
- Providing Cash Flow ensures there is enough money available for businesses and individuals to pay their short-term bills and expenses.
- Helping Control the Money Supply: Central banks use the Money Market to manage the amount of money in the economy. This helps keep prices stable and control inflation.
- Moving Funds Efficiently: The Money Market allows money to flow from those who have extra (like investors) to those who need short-term loans (like companies), supporting economic growth.
- Different from Capital Markets: Unlike capital markets, which deal with long-term investments like stocks and bonds, the Money Market focuses on immediate financial needs. Understanding the difference between the Money Market and capital markets helps investors make better decisions.
- Supporting Global Trade: It helps countries by making it easier to trade with each other by providing a common currency they easily use.
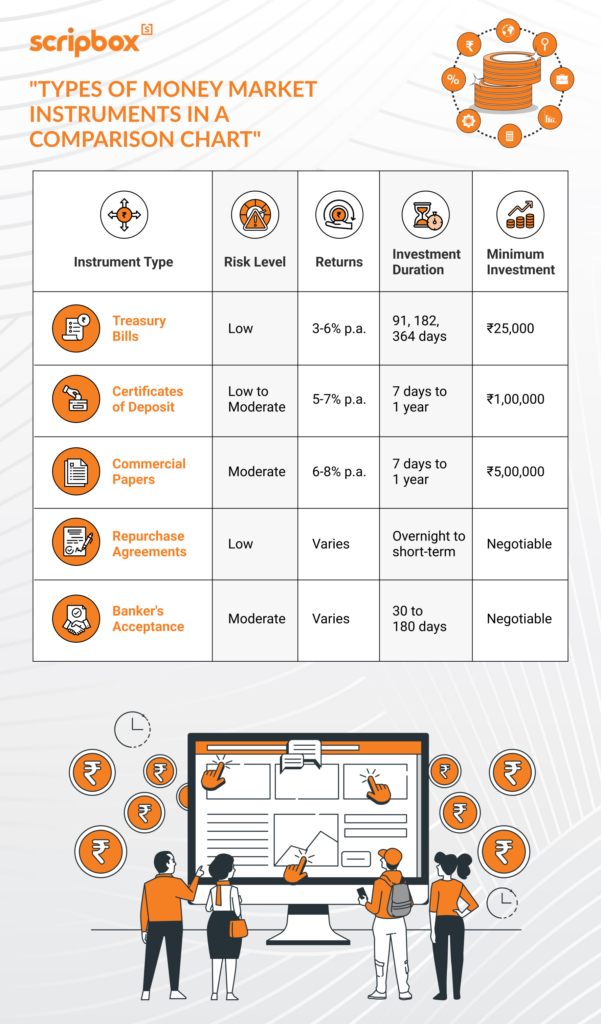
Types of Money Market Instruments
Money Market instruments are tools used to handle short-term cash needs. In the Money Market, people and businesses lend and borrow money for less than one year. Understanding what the Money Market is helps us see how these instruments work. It’s important to know the difference between the Money Market and the capital market: the Money Market deals with short-term funds, while the capital market handles long-term investments like stocks and bonds.
Here are some common types of Money Market instruments:
- Treasury Bills (T-bills) are short-term government bonds that mature in less than a year. They are very safe because the government backs them.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): These are savings accounts where you deposit money for a set time, like six months or a year, and earn interest.
- Commercial Paper is a short-term loan that big companies use to pay for salaries or inventory.
- Call Money Market: In the call Money Market, banks lend money to each other for very short periods, sometimes just one day.
- Repurchase Agreements (Repos) occur when one party sells a security to another and agrees to buy it back later at a higher price.
- Banker’s Acceptances: These are promises that a bank will pay a certain amount at a future date, often used in international trade.
These Money Market instruments are important because they keep the Money Market running smoothly. They help people and businesses manage their money quickly and safely, demonstrating the Money Market’s importance in our economy.
Features of Money Market
The Money Market has special features that make it different from other markets. Knowing what a Money Market is and the difference between a Money Market and a capital market helps us understand these features. Here are some key points:
- Short-Term Transactions: In the Money Market, loans and investments are for less than one year. This is different from the capital market, where investments are long-term.
- High Liquidity: Money Market instruments can be quickly converted into cash, which is important for meeting immediate financial needs.
- Low Risk: Because loans are short-term and borrowers are usually trusted institutions, Money Market instruments are considered low risk.
- Large Participants: The main users of the Money Market are big players like banks, governments, and large companies.
- Call Money Market: This is a part of the Money Market where banks lend to each other for very short times, sometimes overnight.
- Helps Control Money Supply: Central banks use the Money Market to manage the amount of money in the economy, which shows the importance of the Money Market in controlling inflation and interest rates.
Who Can Invest in Money Market Mutual Funds?
- People Seeking Safety with Some Growth: This is ideal for those who want to keep their money safe while earning some interest.
- Individuals with Short-Term Cash Needs: If you have extra cash you might need soon, these funds are a smart choice because they invest in low-risk, short-term Money Market instruments.
- New Investors: Money Market mutual funds are great for beginners because they are easy to understand and less risky than other investments.
- Saving for Short-Term Goals: If you’re saving for things like a car or a vacation, these funds can help your money grow a little more than a regular savings account.
- Businesses Managing Cash Flow: Companies use these funds to earn interest while keeping money available for daily needs.
- Anyone Understanding the Money Market: Knowing what the Money Market is can help you see the usefulness of these funds in managing your finances.
What to Know Before Investing in Money Market Mutual Funds
Not Completely Risk-Free: Although these funds invest in low-risk Money Market instruments, they are not insured like bank accounts, so there’s still a small risk.
Fees Can Reduce Returns: Be aware of any fees that might affect your earnings.
Low Interest Rates: If interest rates are low, you might not earn much more than in a regular savings account.
Liquidity: Ensure you can access your money when you need it without penalties.
Understand the Investment: To make informed decisions, you must know what the Money Market is and the difference between it and the capital market.
Past Performance Isn’t a Guarantee: Just because a fund did well before doesn’t mean it will in the future.
Consult a Professional: Consider talking to a financial advisor before investing.
Pros and Cons of Money Market Instruments
Pros:
- Low Risk: Money Market instruments are safe because they involve short-term loans to trusted groups like governments and big companies.
- High Liquidity: They can be quickly turned into cash, which is helpful for short-term needs.
- Stable Returns: While not huge, the returns are steady, which is good for protecting your money.
- Easy to Understand: Knowing what the Money Market is makes it simple to invest in these instruments.
- Good for Cash Management: Businesses and people can earn a bit of interest on extra cash without taking big risks.
Cons:
- Lower Returns: The earnings are usually less than those from long-term investments in the capital market.
- Inflation Risk: If prices rise fast, the money you earn might not keep up with inflation.
- Not Completely Risk-Free: There is still a tiny chance you could lose money if a borrower can’t pay back.
- Large Investment Needed: Some Money Market instruments require a large amount of money to get started.
- Difference Between Money Market and Capital Market: Understanding this difference is important, as Money Markets are for short-term needs and might not suit long-term goals.
Differences between the Money Market and Other types of markets.
Given our various types of markets, it’s pretty easy to be confused about which is which. Here’s a simple guide to help you distinguish between each of them.
Money Market vs Capital Market
Money Markets handle short-term cash needs with low-risk options like Treasury Bills and Commercial Papers. They offer safe, liquid investments that mature quickly. On the other hand, capital markets deal with long-term investments like stocks and bonds, which come with higher risks but the chance for bigger returns.
In the Money Market, banks and financial institutions seek short-term funding. The capital market includes stockbrokers, mutual funds, investors, and others interested in long-term growth.
Simply put, Money Markets meet immediate cash needs, while capital markets help grow money over a longer time.
For more details, read our article on the difference between money and capital markets.
Money Market Vs. Stock Market
| Particulars | Money Market | Stock Market |
| Maturity of the instruments | The money market instruments carry a maturity period of less than a year. | However tradable in the short term, stocks create wealth creation when invested for a number of years. |
| Financing needs | These instruments are used to fund the short-term needs of the borrower. | Used for long-term fund requirements. |
| Types of instruments | Instruments of money market include T-bills, certificate of deposits, inter-bank call money, etc. | It’s a stock of an independently listed company |
| Degree of risk | Risk is comparatively lower due to the short-term maturity period | Risk is higher. |
How to Determine Interest Rates of Money Market Instruments
Interest rates for Money Market instruments are influenced by several factors. Here’s what affects the rates:
- Supply and Demand in the Money Market: Interest rates can go up when many people or businesses want to borrow using Money Market instruments. If there’s plenty of money available to lend in the Money Market, rates might go down.
- Central Bank Policies: The central bank sets key rates that influence the interest rates of Money Market instruments. This includes rates in the call Money Market, where banks lend to each other.
- Inflation Rates: If prices are rising quickly (high inflation), lenders of Money Market instruments will ask for higher interest rates to avoid losing money in real terms.
- Economic Conditions: In a strong economy, businesses borrow more using Money Market instruments, which can push interest rates up. In a weak economy, borrowing decreases, and rates may fall to encourage more lending in the Money Market.
- Government Borrowing Needs: When the government borrows a lot by issuing money market instruments like treasury bills, interest rates can be affected. More government borrowing can lead to higher rates.
- Global Financial Markets: Events in other countries can impact our Money Market. If foreign Money Market instruments offer higher interest rates, investors might move their money abroad, affecting local rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
A treasury bill (T Bill) is a short term government debt obligation. The Reserve Bank of India issues it. It has a maturity of one year or less. Hence, these are short term instruments. The T-bills are issued to address the liquidity shortfall in the economy.
T-bills are zero-coupon securities. In other words, these instruments do not earn any interest. However, these are issued at a discount to the face value. The difference between the face value and the issue price is the return to the investor.
For example, the face value of a 91day T-bill is INR 100. However, the RBI issues them at a discounted price of INR 95. Upon maturity, the investor would get INR 100. Hence, the return for an investor is INR 5.
Following are the types of T-bills in India:
1. 14-day Treasury bill
2. 91-day Treasury bill
3. 182-day Treasury bill
4. 364-day Treasury bill
Money markets are unorganised markets. Financial institutions, banks, brokers and money dealers trade for a short period. T Bills, commercial paper, certificate of deposit, trade credit, bills of exchange, promissory notes, call money, etc. are some of the examples of money market instruments. These are highly liquid instruments and can be redeemed easily. Most money market trades take place over the counter (OTC).
Capital market deals in financial products such as stocks (equity shares), preference shares, debentures, bonds, etc. These instruments are traded for longer durations. The capital market instruments are used to finance long term capital requirements.
The capital market consists of two categories:
1. Primary Market: A market in which a fresh issue of securities takes place.
2. Secondary Market: A market where securities are traded on the exchange between the investors.
No, a fixed deposit (FD) is not a money market instrument. However, a certificate of deposit is a money market instrument. A certificate of deposit is similar to a fixed deposit as both pay an interest higher than a bank savings account. However, a certificate of deposit is negotiable, and a fixed deposit is not. A certificate of deposit has a higher minimum investment and longer investment horizon than a fixed deposit.
The money market is the component of a financial market that deals with short term borrowings. On the other hand, the capital market is also a component of the financial market that allows long term trading of equity and debt securities.
Money markets deal in short term lending, borrowing, buying and selling. In contrast, capital markets deal in long term lending or borrowing. Corporations or investors with sizeable investible amount deal in capital markets. Financial regulators in India are responsible for overseeing the capital market activities. Their role is to ensure that companies do not default investors.
Businesses are seeking to fulfil short term credit requirements go-to money market. In comparison, capital markets meet the long term financial needs of the business.
Capital markets offer highly volatile instruments. On the other hand, the money market offers comparatively, safer assets. Returns from capital markets are comparatively higher. The returns from capital markets correlate with the volatility (level of risk). However, this is not always the case. Returns from money market instruments are low but steady.
Maturity of money market instruments is usually up to one year. At the same time, the maturity of capital markets instruments is longer. They don’t have a specific time frame.
No investment is risk-free. All investments have different levels of risk associated with them. Money market funds are not inherently risk-free. Following are the risks associated with money market funds:
1. Default Risk (Credit Risk) : Money market instruments carry the risk of default. There is no guarantee that the borrower will repay the amount. Therefore, there is a default risk associated with these instruments.
2. Interest Rate Risk : Fluctuations in the interest rates have an impact on the yields. A higher volatile fund implies that it is exposed to higher interest rate risk. In a scenario where interest rates fall, the opportunity cost of holding this fund can be high.
3. Price Risk : Similar to share price fluctuations, there is a possibility that prices of money markets funds fluctuate too. In other words, there is a chance that the worth of the instrument might be lesser while selling.
4. Liquidity Risk : The inability to sell the instruments will result in liquidity risk. Liquidity risk comes into play when a money market fund experiences major unexplained cash outflows. The fund is forced to sell because there aren’t enough liquid assets used to manage the outflows.
5. Inflation Risk : Similar to other assets, money market funds also carry inflation risk. The returns from these investments may not be able to keep up with the inflation rate in the economy.
Even though the money market instruments do not carry many risks, it would be incorrect to say that they are entirely risk-free. The reason is simple. While getting money is easier for borrowers with an outstanding track record or credit ratings, there is always a possibility that the borrower might default in the repayment. It is always advisable to refer to the credit ratings before investing or trading.
The money market in India is regulated by both the Reserve Bank of India and the Securities u0026 Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
T-bills are one of the most popular money market instruments. This instrument issued comes with varying short-term maturities. The instrument issued by the Government of India comes at a discount for 14 days to 364 days.
The Government of India aims to provide investors with instruments of varying duration. These government securities are also introduced 14 days, 28 days, 91 days and 364 days T-bills on an auction basis
Individuals, banking companies, other corporate bodies (registered or incorporated in India), and unincorporated bodies can invest. Additionally, non-resident Indians (NRIs) and foreign institutional investors (FIIs), etc can also invest in CPs. Foreign Institutional investors can invest in CP subject to the criteria and conditions laid down by SEBI.
Investors including corporations, banking institutions, companies, and individuals can invest in money market instruments. Money market instruments are best suited for the short-term investment objectives of the investors. Hence, an investor who wishes to earn a higher interest rate on their surplus funds must consider these instruments.
The major difference between money market instruments and equity securities is that these instruments are meant to fund short-term capital needs. On the other hand, equity securities are issued to raise capital for the long term. Owning to the intent of the issuing companies the risk and return involved is different as well. Due to the short-term maturity, the risk involved is comparatively lower for money market instruments. The risk associated with equity securities is higher than with money market instruments.
Fixed income instruments are financial instruments that provide a fixed return or interest rate. The interest rate is predetermined and payable at a fixed date. For example, a fixed deposit is a fixed income instrument. It provides interest income at a predetermined rate and date. While money market instruments also provide a fixed return on investment. However, both instruments vary in terms of maturity, risk, and liquidity. Money market instruments have a maturity of less than 1 year providing greater liquidity along with lower credit default risk.
Examples of money market instruments are treasury bills, commercial papers, certificates of deposits, call money, call (overnight), commercial bills and short-notice (up to fourteen days) money, and term money. All these instruments will have a maturity period of less than 1 year.
The money market instruments are issued by government agencies or bodies, banking institutions, financial institutions, companies, and corporations. These entities are large enterprises and thereby the credit default is comparatively lower. These instruments provide a rate of return which is higher than savings account interest rates. All the types of instruments differ in their maturity, rate of return, and other factors. Hence, before investing the investor must always match their investment objectives with these factors. The best money market instrument will be the instrument which is best suited for the investment objective.
No, bonds are not money market instruments. Bonds with a maturity period of more than 1 year are capital market instruments.
No, mutual funds are not money market instruments. Mutual funds belong to the capital market in the economy. However, the money market funds belong to the money market. These funds invest in money market instruments.
The money market instruments are issued by a borrower who wants to raise capital for a short term. These borrowers include government agencies or bodies, banking institutions, financial institutions, companies, and corporations.
RELATED ARTICLES
- What are Money Market Instruments?
- What is the Money Market?
- Objectives of the Money Market Instruments
- Types of Money Market Instruments
- Features of Money Market
- Who Can Invest in Money Market Mutual Funds?
- What to Know Before Investing in Money Market Mutual Funds
- Pros and Cons of Money Market Instruments
- Differences between the Money Market and Other types of markets.
- How to Determine Interest Rates of Money Market Instruments
- Frequently Asked Questions






















Show comments