Personal Finance. Simplified
Helping you plan your finances better.
2nd
most influential
financial services brand
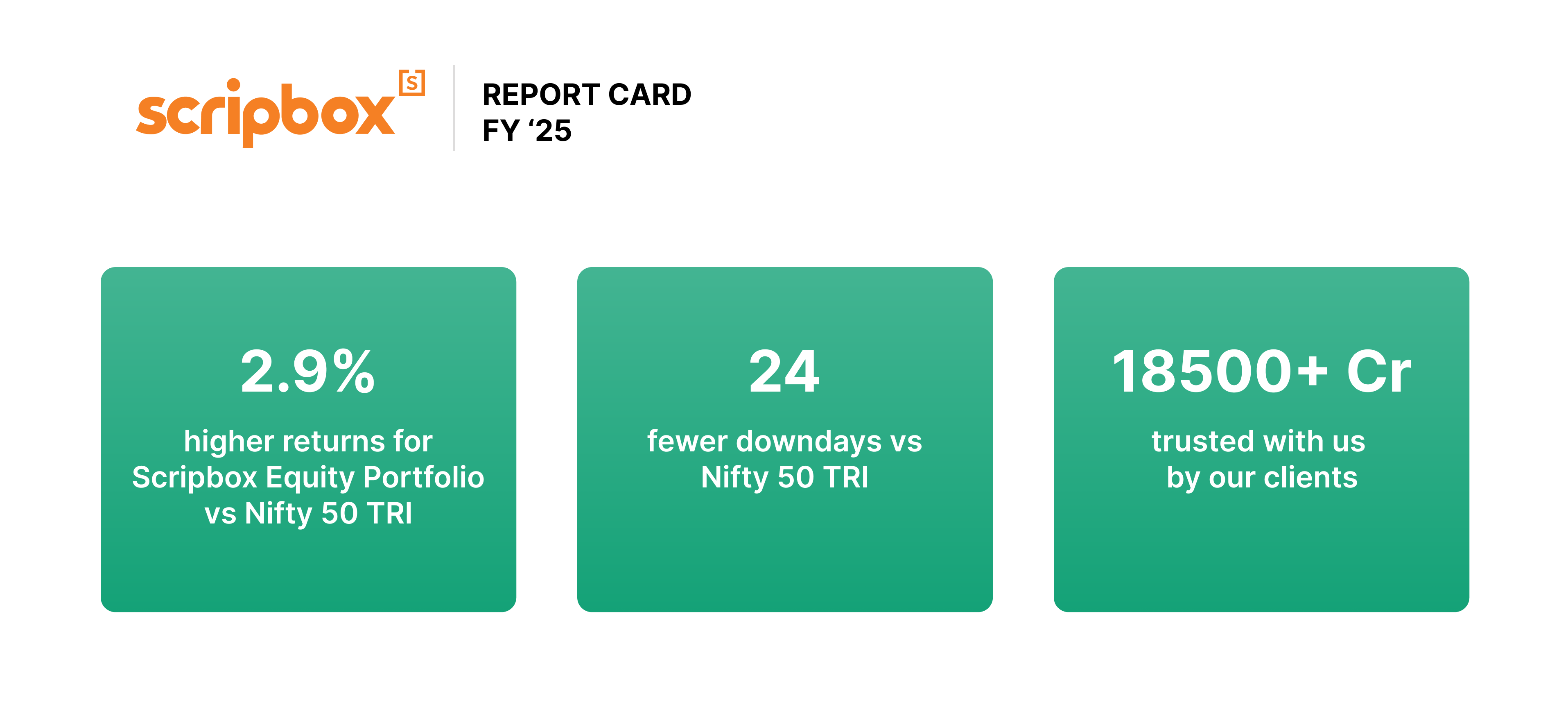
150,000+
Monthly readers
100,000+
Happy investors
18,500 Cr+
AUM Handled

From the
Editor's Desk.
Our Finance Planners
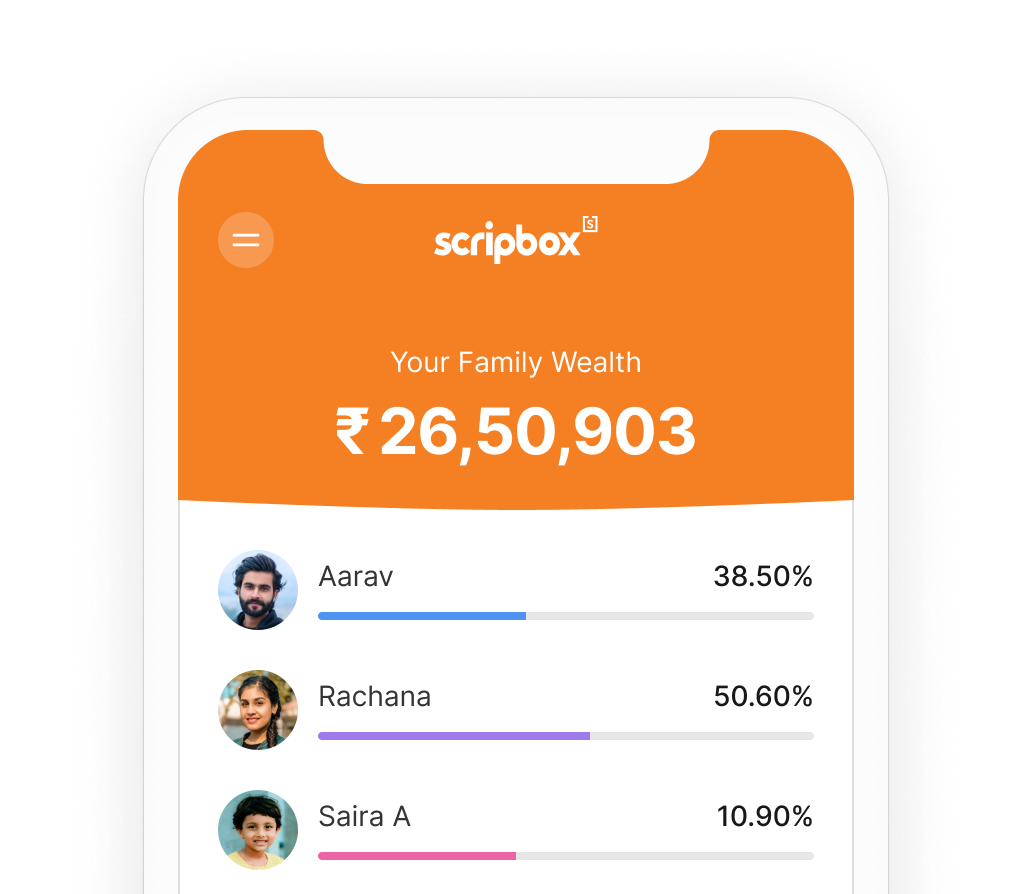
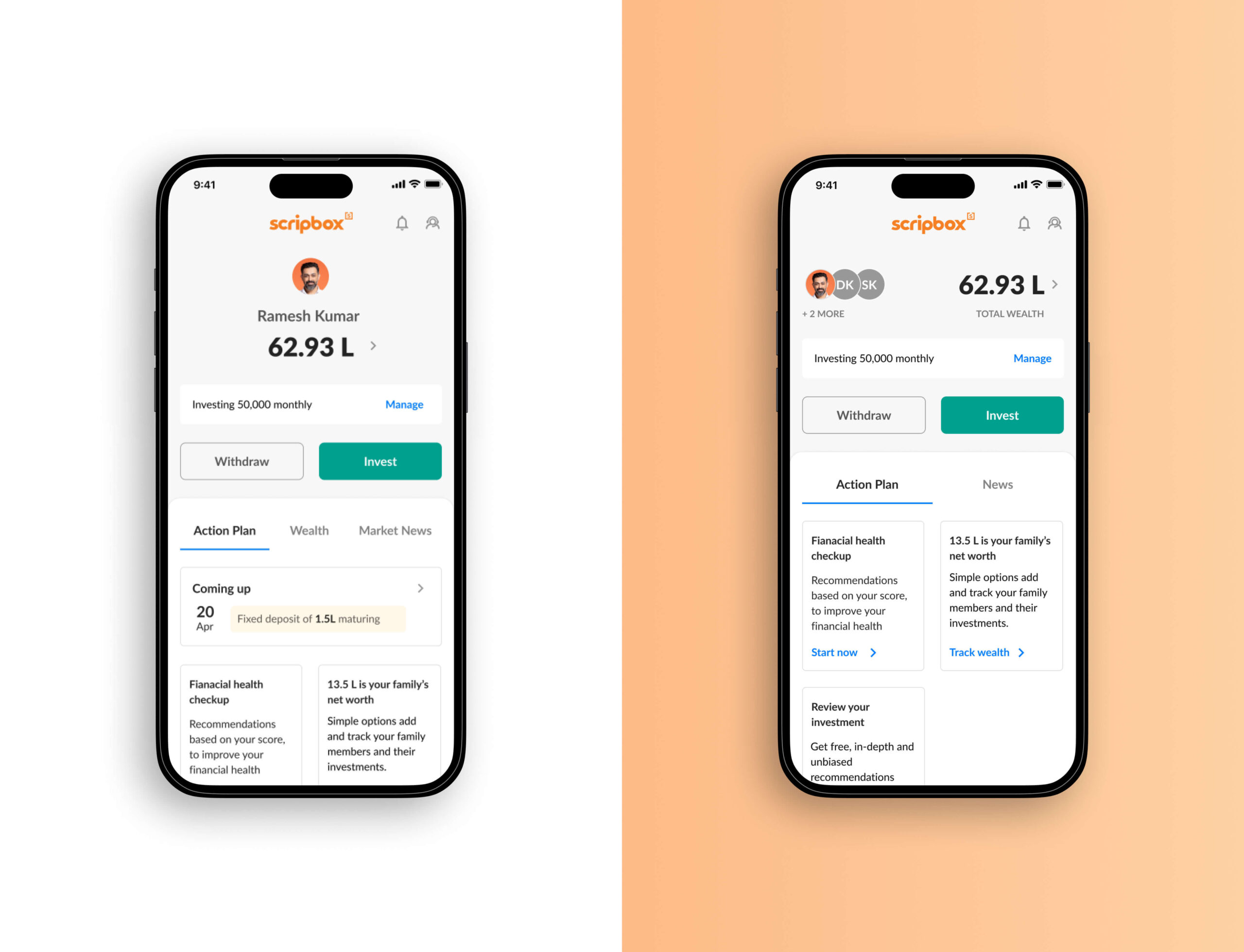
One home, and one app, for all your wealth
View, analyse, manage, and invest your and your family's wealth with the all-new Scripbox App.
One home, and one app, for all your wealth
View, analyse, manage, and invest your and your family's wealth with the all-new Scripbox App.